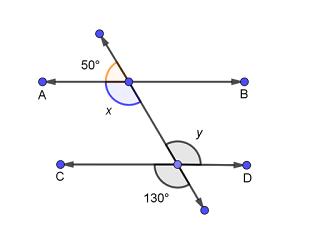
Q1.
In the given figure, find the values of x
and y and then show that AB ‖ CD.
Given:
Figure
To
prove: AB ‖ CD
Proof: 50°
+ x = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ x = 180° – 50° = 130°
Now, y = 130° (Vertically opposite angles)
∴ x = y = 130°
But they are alternate interior angles
∴ AB ‖ CD
Q2.
In the given figure, if AB ‖ CD, CD ‖ EF and y:z = 3:7, find x.
Given: AB ‖ CD, CD ‖ EF and y:z = 3:7
To
find: x
Solution: Let
y = 3a and z = 7a
AB ‖ CD and CD ‖ EF [Given]
AB EF
x = z = 7a
(Alternate interior angles)
Now, x + y = 180° (Co-interior angles)
7a +3a = 180°
10a = 180°
a =
18°
x = z = 7a
= 7 x 18° = 126° Ans.
Q3. In
the given figure, if AB ‖ CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GEF
= 126°, find ∠AGE,
∠GEF
and ∠FGE.
Given: AB ‖ CD, EF ⊥CD and ∠GEF
= 126°
To
find: ∠AGE,
∠GEF and ∠FGE
Solution: AB ‖ CD (Given)
∴ ∠AGE = ∠GED = 126° Ans. (Alternate interior angles)
∠GEF = ∠GED – 90° = 126° – 90° = 36° Ans.
Now, ∠FGE + ∠GED = 180° (Co-interior
angles)
∴ ∠FGE = 180° – 126° = 54° Ans.
Q4.
In the given figure, If PQ ‖ ST, ∠PQR
= 110° and ∠RST
= 130°, find ∠QRS.
Given: PQ ‖ ST, ∠PQR = 110° and ∠RST = 130°
To
find: ∠QRS
Construction:
Draw a line AB ‖ ST through point R
Solution: PQ ‖ ST and AB ‖ ST (Given)
∴ PQ ‖ AB
∠PQR
+ ∠QRA = 180° (Co-interior
angles)
⇒ 110° + ∠QRA = 180°
⇒ ∠QRA
= 180° – 110°
⇒ ∠QRA
= 70°
Now, ∠RST
+ ∠SRB = 180° (Co-interior
angles)
⇒ 130°
+ ∠SRB = 180°
⇒ ∠SRB
= 180° – 30°
⇒ ∠SRB
= 50°
Now, ∠QRA
+ ∠QRS + ∠SRB = 180° (AB is a straight
line)
⇒ 70°
+ ∠QRS + 50° = 180°
⇒ 120°
+ ∠QRS + 50° = 180°
⇒ ∠QRS
= 180° – 120° = 60° Ans.
Q4. In
the given figure, if AB ‖ CD, ∠APQ
= 50° and ∠PRD
= 127°, find x and y.
Given: AB ‖ CD, ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PRD = 127°
To
find: x and y
Solution: ∠APQ = ∠PQR (Alternate interior
angles)
∴ x = 50° Ans.
Now, ∠PRQ
+ 127° = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ ∠PRQ
= 180° - 27° = 53°
Now, x + y + ∠PRQ = 180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)
⇒ 50°
+ y + 53° = 180°
⇒ 103°
+ y = 180°
Given: PQ
and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other
To
prove: AB ‖ CD
Construction:
Draw BX ⊥ PQ and CY ⊥ RS
Proof: ∠ABX
= ∠CBX and ∠DCY = ∠BCY [Angle of incidence =
Angle of reflection]
But ∠CBX
= ∠BCY (1) (Alternate interior
angles)
∴ ∠ABX
= ∠DCY (2)
Adding (1) and (2), we get
∠CBX
+ ∠ABX = ∠BCY + ∠DCY
⇒ ∠ABC
= ∠DCB
But they are alternate interior angles
∴ AB ‖ BC